Netrina-1: Su posible uso terapéutico sobre el desarrollo de la aterosclerosis / Netrina-1: Its posible therapeutic use on the development of atherosclerosis
Palabras clave:
Aterosclerosis; monocito; macrófagos; netrina-1Resumen
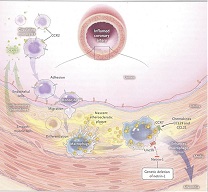
Se efectuó una revisión bibliográfica de 14 artículos científicos y dos libros de textos, sobre los procesos patológicos que contribuyen en la formación de la aterosclerosis y se hizo una valoración sobre los efectos de la Netrina-1 sobre la patogenia de dicho trastorno, así como su posible uso terapéutico. La aterosclerosis es clínicamente importante ya que constituye la base de la patogenia de las enfermedades coronarias, las cuales presentan una alta tasa de morbilidad y mortalidad en relación con cualquier otro trastorno en el mundo occidental. La causa del desarrollo de la aterosclerosis es multifactorial ya que incluye varios factores como: el estilo de vida del individuo, los factores biológicos y los genéticos. En los años recientes se ha demostrado que la proteína Netrina-1 es un modulador clave para los procesos patológicos de la aterosclerosis ya que, inhibe la formación de la placa ateroma. Una placa de ateroma constituye fundamentalmente depósito de colesterol elevada en la túnica íntima. Por tanto, se ha demostrado que el rol de los monocitos en el desarrollo de aterosclerosis así como la administración de Lipoproteína de alta densidad o High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) son factores potenciales para la intervención terapéutica. Por lo tanto, muchos de los avances médicos están dirigidos a la cura de diversas de las patogenias conducidas por estos trastornos cardiovasculare. Palabras clave: Aterosclerosis; monocito; macrófagos; Netrina-1. Abstract A bibliography revision was carry out in 14 articles and two books about the pathological processes that contributes in the formation of the atherosclerosis and they valorized the effects of the netrina-1 about the pathogen and its possible therapeutic use. The atherosclerosis is clinically important because it constitutes in the base of the pathogen of the chronic diseases that presents a high rate of morbidity and mortality in relation with whichever other disease in the occidental world. The cause of the development of the atherosclerosis is multifactorial that includes different factors like: individual lifestyle, biological factors and genetics. The past years they demonstrated that the netrina-1 protein is a key modulator for the pathological process of atherosclerosis since it inhibits the formation of the atheroma plate. An atheroma plate is mainly a deposition of elevated cholesterol in the intimate tunic. Therefore, it has been shown that the role of monocytes in the development of atherosclerosis as well as the high-density lipoprotein administration is potential factors for therapeutic intervention. Therefore, many of the medical advances are aimed at the cure of various pathogens conducted by these cardiovascular disorders. Key words: atherosclerosis; monocytes; macrophages; netrina-1.Citas
1. World Health Organizations (WHO). Cardiovascular diseases [Internet]. 2016 [citado marzo 4 2017].Disponible en: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317/es/
2. Kumar V, Abbas AK, Fausto N, Aster J: Robbins. Basic Pathology. 10th. Ed. Philadelphia: Elseviers Saunders; 2017. Cap 10, p 369-378
3. Hidalgo R. Nancy, et al. Patología general: Editorial Ciencias Médicas, La Habana, Cuba. 2014.Cap 8, p. 149-154
4. Gerszten R. E, A. M. Tager. The monocyte in Atherosclerosis-Should I stay or should I go now? N Engl J Med 2012;366:1734-36
5. K. Layne et al. Netrin-1 as a novel therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease: to actívate or inhibit?. Cardiovascular Research 2018; 107:410-419.
6. Moore J. Kathryn. Fisher A. Edward. Macrophages, aterosclerosis and the potential of netrin as a novel target for future therapeutic intervention. National institute of health. New York, NY.2016
7. Khan JA, Cao M. Kang BY, Liu Y, Mehta JL, Hermonat PL. Systemic human Netrin-1 gene delivery by adeno-associated virus type 8 alters leukocyte accumulation and atherogenesis in vivo. Gene Ther 2011; 18:437-444.
8. Randolph GJ. The fate of monocyte in atherosclerosis J Thromb Haemost. 2009; 7(Suppl 1): 28-30
9. Jaipersad AS, Lip GY, Silverman S. The role of Monocytes in Angiogenesis and Atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014; 63(1):1-11.
10. Feig JE. Regression of Atherosclerosis: Insights from Animal and Clinical Studies. Ann Glob Health. 2014; 80(1): 13-23.
11. Chawla A, Repa JJ, Evans RM, Mangelsdorf DJ. Nuclear receptors and lipid physiciology: opening the X-files. Science. 2001; 294: 1866-70.
12. Beaven SW, Tontonoz P. Nuclear receptors in lipid metabolism: targeting the heart of dyslipidemia. Annu Rev Med. 2006; 57: 313-29.
13. Hilgendorf I, Swirski F, Robbins C. Monocyte Fate in Atherosclerosis. Aterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015; 35: 272-279.
14. Ghattas A, Griffiths HR, Devitt A, Lip GY, Shantsila E. Monocytes in Coronary Artery Disease and Atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013; 62(17):1541-51.
15. Tardif JC, et al. Effects of reconstituted high-density lipoprotein infusions on coronary atherosclerosis: a randomized controlled trial. Jama. 2007; 297(15):1675–82
16. Camaré C, Pucelle M, Nègre-Salvayre A, Salvayre R. Angiogenesis in the atherosclerotic plaque. Redox Biology. 2017; 12: 18-34.